Mastering pleural tap: your guide to success
Strasbourg, September 29, 2025
Performing a pleural tap is a skill that calls for precision, training, and confidence. The level of difficulty varies depending on several factors—such as the patient’s morphology (obesity, chest deformities, etc.), their ability to cooperate, the volume of fluid, and of course, the practitioner’s experience.1
To succeed, one must master clinical landmarks, adapt techniques to imaging, and have a strong understanding of anatomy to minimize pain and avoid complications.
For instance, the intercostal neurovascular bundle runs along the lower edge of each rib. If injured during the procedure, it can cause sharp pain, bleeding, or even a vagal reaction.2
That’s why inserting the needle just above the upper edge of the rib is crucial for safe and effective practice.3
Why simulation matters in learning pleural tap?
Pleural tap remains the only minimally invasive way to collect pleural fluid—making it an essential skill for healthcare professionals. Yet, training often still relies on the old model of “see one, do one, teach one.” As highlighted in the comic La vie de Carabin (2013), a medical student recalls performing his first pleural tap without proper training—causing unnecessary pain to the patient.
The French National Health Authority (HAS) has been clear since 2012: “never the first time on a patient.” Instead, simulation-based learning should be the standard.4
With simulation, students benefit from hands-on, risk-free practice, applying theory to realistic clinical scenarios.
They can repeat procedures, sharpen their anatomical knowledge, and understand the impact of poor positioning—turning mistakes into valuable learning opportunities. Simulation builds confidence, reduces stress, and prepares learners to perform pleural taps with control and care.
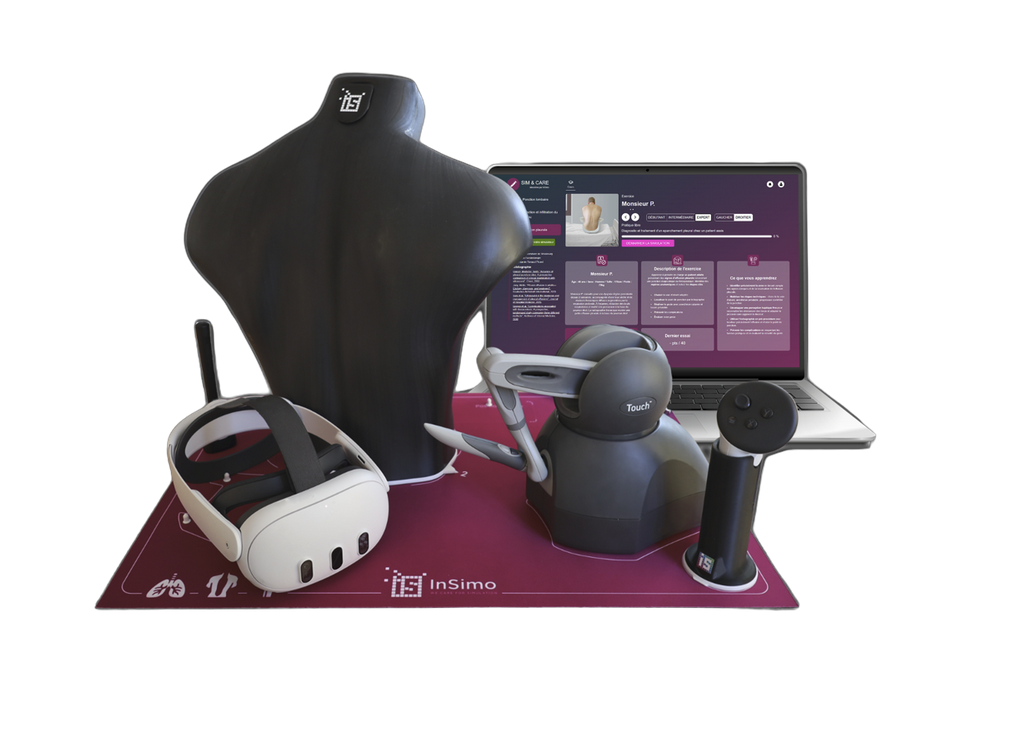
Sim&Care | Chest: Train Smarter with Augmented Reality
Why choose Sim&Care | Chest for training?
Sim&Care |Chest
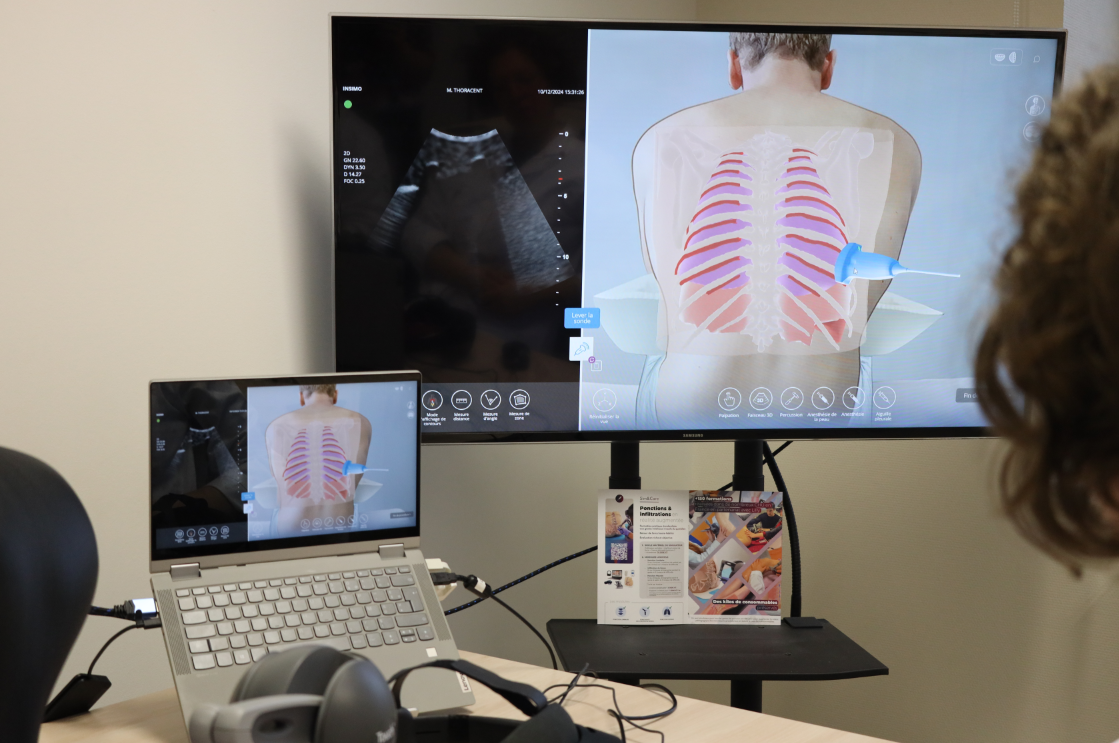
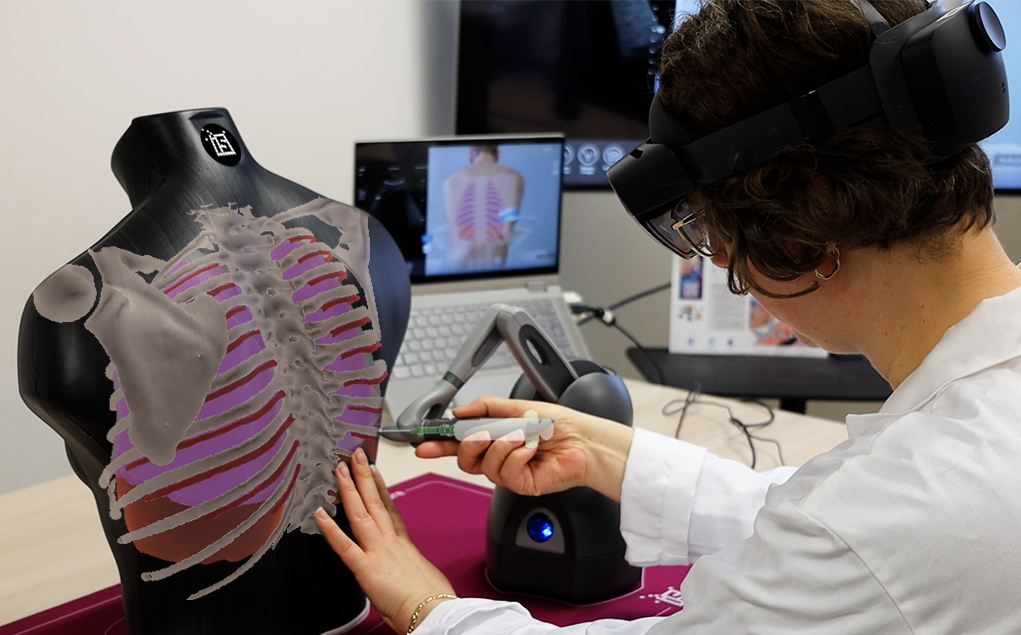
Our Sim&Care simulator is designed to make learning pleural tap both effective and engaging. With 3D anatomical models and biomechanical simulation, it replicates the true resistance of tissues during needle insertion—from skin to pleural cavity. It offers 3 fluid volumes and 2 thoracic orientations, so learners can adapt their technique to different clinical situations.
From lung ultrasound to the invasive procedure itself, Sim&Care guides learners step by step, developing both clinical reasoning and technical skills. Augmented reality adds an extra layer of safety and understanding, allowing users to visualize anatomical structures in transparency while practicing. The simulator also provides detailed feedback, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement—helping learners gain confidence with every session.
Pleural tap is both a common and vital procedure, bridging diagnosis and treatment. When performed correctly, it relieves the patient and guides the next steps of care. That’s why proper hands-on training is so important. By combining technical skill-building with immersive simulation, Sim&Care empowers students to train safely, reduce stress, refine their technique, and ultimately deliver higher-quality care with greater patient safety.

